lv non compaction family screening | Left Ventricular Noncompaction: lv non compaction family screening Isolated left ventricular non-compaction (ILVNC), dilated cardiomyopathy (DCMO) and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) are diseases that may be present in family members of . Sinoć se na Venecija film festivalu na premijeri filma "Lord of the Ants" pojavio i maneken i glumac Alesandro Eger (31), inače rođeni Beograđanin, a društvo mu je .
0 · The Importance of Genetic Counseling, DNA
1 · Left ventricular noncompaction − Risk stratification
2 · Left Ventricular Noncompaction: New Insights into a Poorly
3 · Left Ventricular Noncompaction:
4 · Left Ventricular Non
5 · Isolated left ventricular noncompaction in adults: Clinical
6 · Genetic Basis of Left Ventricular Noncompaction
7 · Family screening in black patients with isolated left ventricular non
8 · Determination of Genotype and Phenotypes in Pediatric Patients
9 · Clinical Risk Prediction in Patients With Left
Alegerea: Acceptă cu bucurie posibilul. Edith Eger, Edith Eva Eger. 4.58. 101,991 ratings10,093 reviews. La 16 ani, Edith Eger a fost trimisă la Auschwitz. La câteva ore după ce părinții i-au fost gazați, ofițerul nazist dr. Josef Mengele a forțat-o pe Edie să danseze, și a lăsat-o în viață ca să-l distreze.
Left ventricular noncompaction (LVNC) describes a ventricular wall anatomy characterized by prominent left ventricular (LV) trabeculae, a thin compacted layer, and deep .LVEF by TTE was 48% ± 17% and 79 patients had myocardial fibrosis assessed by LGE (18.
This review will focus on clinical manifestations and diagnosis of LVNC as an isolated disorder distinct from other clinical settings in which non-compacted myocardium may .Isolated left ventricular non-compaction (ILVNC), dilated cardiomyopathy (DCMO) and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) are diseases that may be present in family members of .
Clinical manifestations of left ventricular non-compaction (LVNC) are highly variable even in the same family, ranging from no symptoms to disabling congestive heart failure, life-threatening arrhythmias, systemic thromboemboli, .In asymptomatic patients, LVNC is identified by echocardiography or when the patient is subjected to family screening. However, when the disease is identified during the fetal period, . Accordingly, the diagnosis of LVNC requires genetic counseling, DNA diagnostics, and cardiological family screening. Left ventricular noncompaction (LVNC) is a cardiomyopathy featuring segmental thickening of . Experimental data supports the hypothesis that LVNC is caused by disruption of 2 morphological events that are essential for generating a functional myocardium: ventricular trabeculation and myocardial compaction.
LVEF by TTE was 48% ± 17% and 79 patients had myocardial fibrosis assessed by LGE (18% of those with CMR). Family screening was completed in 253 (58%) probands (most other relatives refused to undergo screening), being positive .
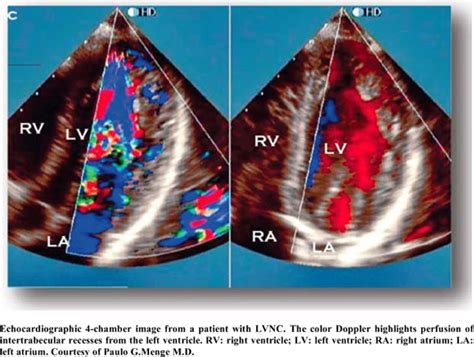
Left ventricular noncompaction (LVNC) is a heterogeneous myocardial disorder characterized by prominent trabeculations, intratrabecular recesses, and division of the left .
Left ventricular non-compaction (LVNC) cardiomyopathy is a condition where your lower left heart chamber (left ventricle) doesn’t develop properly. Instead of being firm and .Left ventricular noncompaction (LVNC) describes a ventricular wall anatomy characterized by prominent left ventricular (LV) trabeculae, a thin compacted layer, and deep intertrabecular recesses. Individual variability is extreme, and trabeculae represent a . This review will focus on clinical manifestations and diagnosis of LVNC as an isolated disorder distinct from other clinical settings in which non-compacted myocardium may be seen in association with other cardiac and noncardiac abnormalities. Management and prognosis of isolated LVNC is discussed separately.Isolated left ventricular non-compaction (ILVNC), dilated cardiomyopathy (DCMO) and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) are diseases that may be present in family members of patients with ILVNC. The primary aim of this study was to identify the prevalence and spectrum of cardiomyopathy in first-degree relatives of patients with ILVNC.
Clinical manifestations of left ventricular non-compaction (LVNC) are highly variable even in the same family, ranging from no symptoms to disabling congestive heart failure, life-threatening arrhythmias, systemic thromboemboli, and sudden cardiac death.In asymptomatic patients, LVNC is identified by echocardiography or when the patient is subjected to family screening. However, when the disease is identified during the fetal period, the presence of systemic diseases, such as mitochondrial alterations and metabolic disorders, is frequently reported [8]. 4. GENETICS. Accordingly, the diagnosis of LVNC requires genetic counseling, DNA diagnostics, and cardiological family screening. Left ventricular noncompaction (LVNC) is a cardiomyopathy featuring segmental thickening of the LV wall with a thin, compact, epicardial layer and an excessively thickened endocardial layer with prominent, deep intertrabecular . Experimental data supports the hypothesis that LVNC is caused by disruption of 2 morphological events that are essential for generating a functional myocardium: ventricular trabeculation and myocardial compaction.
LVEF by TTE was 48% ± 17% and 79 patients had myocardial fibrosis assessed by LGE (18% of those with CMR). Family screening was completed in 253 (58%) probands (most other relatives refused to undergo screening), being positive in 106 (42%). Left ventricular noncompaction (LVNC) is a heterogeneous myocardial disorder characterized by prominent trabeculations, intratrabecular recesses, and division of the left ventricular myocardium into 2 compacted and noncompacted layers. 1, 2 LVNC mainly affects the left ventricle (LV); however, isolated right ventricular noncompaction (RVNC) and biventricular . Left ventricular non-compaction (LVNC) cardiomyopathy is a condition where your lower left heart chamber (left ventricle) doesn’t develop properly. Instead of being firm and smooth, the left ventricle is spongy and thick.

Left ventricular noncompaction (LVNC) describes a ventricular wall anatomy characterized by prominent left ventricular (LV) trabeculae, a thin compacted layer, and deep intertrabecular recesses. Individual variability is extreme, and trabeculae represent a . This review will focus on clinical manifestations and diagnosis of LVNC as an isolated disorder distinct from other clinical settings in which non-compacted myocardium may be seen in association with other cardiac and noncardiac abnormalities. Management and prognosis of isolated LVNC is discussed separately.Isolated left ventricular non-compaction (ILVNC), dilated cardiomyopathy (DCMO) and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) are diseases that may be present in family members of patients with ILVNC. The primary aim of this study was to identify the prevalence and spectrum of cardiomyopathy in first-degree relatives of patients with ILVNC.
Clinical manifestations of left ventricular non-compaction (LVNC) are highly variable even in the same family, ranging from no symptoms to disabling congestive heart failure, life-threatening arrhythmias, systemic thromboemboli, and sudden cardiac death.In asymptomatic patients, LVNC is identified by echocardiography or when the patient is subjected to family screening. However, when the disease is identified during the fetal period, the presence of systemic diseases, such as mitochondrial alterations and metabolic disorders, is frequently reported [8]. 4. GENETICS.
The Importance of Genetic Counseling, DNA
Left ventricular noncompaction − Risk stratification
Accordingly, the diagnosis of LVNC requires genetic counseling, DNA diagnostics, and cardiological family screening. Left ventricular noncompaction (LVNC) is a cardiomyopathy featuring segmental thickening of the LV wall with a thin, compact, epicardial layer and an excessively thickened endocardial layer with prominent, deep intertrabecular .
Experimental data supports the hypothesis that LVNC is caused by disruption of 2 morphological events that are essential for generating a functional myocardium: ventricular trabeculation and myocardial compaction.LVEF by TTE was 48% ± 17% and 79 patients had myocardial fibrosis assessed by LGE (18% of those with CMR). Family screening was completed in 253 (58%) probands (most other relatives refused to undergo screening), being positive in 106 (42%).

Left Ventricular Noncompaction: New Insights into a Poorly
Left ventricular noncompaction (LVNC) is a heterogeneous myocardial disorder characterized by prominent trabeculations, intratrabecular recesses, and division of the left ventricular myocardium into 2 compacted and noncompacted layers. 1, 2 LVNC mainly affects the left ventricle (LV); however, isolated right ventricular noncompaction (RVNC) and biventricular .
Left Ventricular Noncompaction:
Left Ventricular Non
Black smooth calf leather sneaker with rounded toe and tonal black heel panel. Perforated air holes, large flat laces and Alexander McQueen signature on tongue and heel. Leather lined. Tonal black oversized rubber sole.
lv non compaction family screening|Left Ventricular Noncompaction: